Wärtsilä Marine Methanol Conversion
The maritime industry is currently looking into alternative fuels and fuel flexibility in order to cut greenhouse gas and other emissions. One of the emerging alternative step towards decarbonised operations in the form of alternative, greener future fuels is methanol. Methanol meet current and future emissions targets in terms of NOx, SOX and particulates, and there’s a readily available global supply which makes methanol a viable fuel for any type of marine vessel.
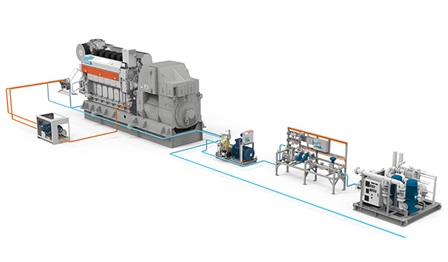
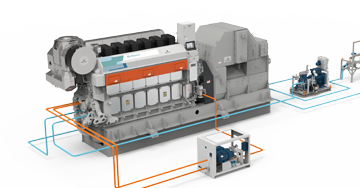
Wärtsilä Marine Methanol Conversion is a holistic solution for converting a vessel to use methanol as a fuel. Whether your vessel can be converted to run on methanol depends very much if there is enough space on board.
Why? Because methanol is less energy-dense than conventional fuel, it requires larger tanks. The methanol engine still needs pilot fuel for ignition, so another, smaller fuel supply system is necessary. The double-walled fuel piping for methanol also takes up a bit more space than before.
Wärtsilä can support you throughout the project starting from a feasibility study and the feasibility calculations to a full project execution.
Professional support
Engine conversion technology is currently available for ZA40S engines and will soon be available for Wärtsilä 32 and Wärtsilä 46F engines.
Wärtsilä can support you throughout the conversion project – from a feasibility study complete with business case calculations to execution planning and the successful conversion. Wärtsilä’s professional project management teams have a proven track record of running smooth, successful projects.
Your benefits from this fuel conversion
- Reduction of emissions
- Compliance with regulations
- Greener image
- Increased fuel flexibility
Your easiest next step
When you are thinking about a fuel conversion for your vessel, start here. Learn the five important things to consider and you will be better prepared for the conversion project.
Download white paper
4 clear examples - proof that methanol could really work for your vessel
Discover four real-life examples – one each from the cruise, ferry, merchant and offshore sectors. Learn how operators are already using methanol to solve their challenges, and how you can start using it to reduce emissions immediately.
Customer references
Methanol conversion will reduce emissions
Converting your vessel’s engines to run on methanol is a great way to reduce your emissions. You will find 49 more ways in a fascinating eBook “50 great ways the maritime industry could cut its greenhouse gas emissions”. Learn more: